
MARCH OF THE TITANS - A HISTORY OF THE WHITE RACE
CHAPTER 21 : THE SECOND GREAT RACE WAR - THE CRUSADES
The rise of Islam from a tiny cult in Saudi-Arabia to the status of a major world power is a factor which has dominated much of White history from around 800 AD right through to the present day - indeed, many of the growing conflicts in the contemporary world can be ascribed to this militant and fierce religion.
Although Islam, like Christianity, originated in the Semitic world, and is thus formally outside the scope of this book, it is however, like Christianity, vital to understand this religion as it has played, and continues to play, an important role in affecting European history.
Started by an Arab, Mohammed, (570 AD - 632 AD) in the Arabian peninsula (today's Saudi Arabia) around the year 590 AD, Islam is essentially a reworking of Judaism and Christianity (the Muslim God, Allah, is identified in the Muslim holy book, the Koran, as the same one in Judaism and Christianity) and all three religions share many of the same Old Testament characters such as Jacob etc..
The Koran even features Jesus Christ, only differing with Christianity by saying that Christ was not the son of God but just another prophet like the others mentioned in the Old Testament. It is presumed, but unproven, that Mohammed gained his knowledge of Judaism and Christianity from his Jewish wife.
Mohammed was by all accounts a dynamic person. Claiming to be God's final and true prophet, he persuaded large masses of people that he was right. Pulling together the scattered strands of Judaism and Christianity and then mixing it with some original Arabic customs, he created a powerful religious message which encouraged its supporters to convert others on pain of death.

Although fought under the guise of Christianity, the Crusades were in fact an overt race war. White armies set off from all over Europe to drive the Nonwhites out of the Middle East. Here St. Bernard preaches the Second Crusade - there were varying degrees of response, but possibly one of the most interesting by-products of the Crusades was a flare up in anti-Jewish sentiment in Europe, as Jews were associated with the Muslims in Palestine. Indeed, when Jerusalem was finally conquered by the White Crusaders, they proceeded to massacre all Muslims and Jews alike.
ISLAM EXPANDS BY FORCE
Swiftly the followers of his religion subdued first the Arabian peninsula. They then turned their attention to the neighboring territories (then still formally part of the Eastern Roman Empire) and in quick succession occupied Syria, Iraq, Persia and a large slice of Turkey.
In 640 AD, Egypt, then still part of the Eastern Roman Empire, was overrun by the Islamic armies. Expanding westwards along the North African coast, by 711 AD, the Muslims crossed the straits of Gilbratar and entered Spain, penetrating into Southern France, where they were eventually turned back in 732 AD at the Battle of Tours.
ASSAULT ON BYZANTINE - CONSTANTINOPLE HOLDS OUT
The Eastern Roman Empire viewed the rise of Islam with alarm. Forgetting that the God of the Christian Bible was the same being as the Allah in the Koran and instead dealing with the reality that a blatant racial war was brewing between the Nonwhite Muslims and White Europe, the Eastern Romans immediately tried to prevent the spread of the new religion.
They were however fighting a hopeless rear guard action at best. Facing fanatical Muslim warriors engaging in a Jihad, or Holy War, the Eastern Roman army, not even a shadow of the former armies of Imperial Rome, could not hold back the tide.
By 1071, the Byzantine armies were defeated at the Battle of Manzikert, and all of Turkey fell to Islam and the Seljuk Turks, leaving only Constantinople at the very western part of that country as a small Christian citadel defying the Islamic giant in the east.
Simultaneously the Bulgars, Asiatics invaders from the East, had been pressing Constantinople from the Balkans. Although they were also temporarily turned back by the emperor Basil II (known as the "Bulgar-Slayer" - he once blinded 1500 captured Bulgars and sent them marching back to the enemy camp with only a few one eyed guides) they kept up a continual pressure from the Balkans.
By the end of the year 1001 AD, the Eastern Roman Empire, Byzantine, consisted of little more than the immediate territory surrounding the city of Constantinople itself.
EASTERN EMPIRE FALLS TO TURKS - 1453 AD
By 1250 AD, a new wave of Islamic soldiers, the Ottoman Turks, had emerged from Asia Minor. They crashed through the Christian defenses and finally in 1453, Constantinople itself fell to Islam.
The Eastern Roman Empire formally came to an end, but of course, like Rome, the last true Romans had vanished many hundreds of years earlier, and the Islamic armies were only held off for as long as they were by the use of large numbers of White European mercenaries and volunteers - the city itself was largely inhabited by people who were, like the Turks, largely racially mixed.

The tomb of a Crusader Knight in Dorchester Abbey, England. The Knight has been captured at the moment of death, his face in a grimace as he tries to pull his sword from its scabbard. The name of the knight is unknown, but that he was a Crusader is unquestioned - all Crusader tombs of this nature had the convention of crossed legs as their identifying marker.
THE CRUSADES - 200 YEARS OF RACE WAR
In the period leading up to the fall of Constantinople, the second major overtly racial war between the White race and the Middle Eastern mixed races broke out, taking the form of a series of armies attacking the nations of Islam in a period running for nearly 200 years: from 1095 to the middle of the thirteenth century.
Originally the term Crusade was applied only to the White Christian efforts to capture the city of Jerusalem in Palestine from the Muslims, but very soon it came to refer to any military effort by the Whites against the darker races of the Middle East.
Some in Europe seized the opportunity to attack Jews in mainland Europe itself at the same time, associating them with the Muslims in Palestine and then in Islamic Moorish occupied Spain and elsewhere.
The Crusaders also created a series of relatively short lived feudal states in the Near East, the first European colonies outside the European mainland.
THE POPE
It was the growth in the power of the church which created the political unity which made it possible for White Europe to go on the offensive against the Nonwhite invasion.
In particular it was the reverence for the Pope as head of the Christian church which played a crucial role in getting the increasing number of Christian heads of state in Western Europe to take up arms.
While religious motivation was most certainly the prime driver of the initial crusades, there was also a very clear racial undercurrent which ran through the three centuries of warfare.
It is important to appreciate that the hostilities between the White Christians and the mixed race Arabic/Semitic Muslims was initiated by the Nonwhites.
Just before the reign of the Frankish king Charlemagne, who died in 814 AD, Europe had suddenly been subjected to unprovoked, violent attack by the Nonwhite Muslim world.
MUSLIM ATTACKS
By 700 AD, Islamic armies had occupied North Africa and had destroyed what remained of the Gothic Vandal state.
The eastern shores of the Mediterranean, and most of Spain had been overrun by Islamic Nonwhite armies from the Saudi Arabian peninsula. Islamic armies established bases in Italy, and were closing in on Constantinople. On all fronts, the Muslims seemed unstoppable.
APPEAL FROM POPE URBAN II
The idea of the crusades started officially with a speech by Pope Urban II at Clermont in France in November 1095. The Pope spoke about the advance of Islam, and called for a great Christian expedition to free Jerusalem from the newest Muslim nation to occupy the Middle East and Asia Minor, the Seljuk Turks (who were also threatening Constantinople - the then Byzantine emperor, Alexius I, had called on Western Christendom for help). These Muslims had also started attacking Christian pilgrims traveling to Palestine to visit sites holy to their religion.
Pope Urban's message spread like a holy quest, and almost immediately the White nations started preparing for what was to become a three century long race war.
THE FIRST CRUSADE (1095 - 1099 AD)
The First Crusade had as its explicit aim the capture of the city of Jerusalem in Palestine from the Muslims. In this aim it was successful - and the White Christians managed to hang on to an outpost in Palestine for very nearly two hundred years before finally being driven out by the Muslims.
The First Crusade did not attract any kings and very few nobles - most were middle class French speakers - which was why Whites in Palestine were referred to as Franks.
The First Crusade suffered however from internal organizational problems - it had no leader, no formal arrangement with Constantinople and also little idea of what else to do apart from occupying Jerusalem. The different groups used different routes to get to Constantinople, the kick off place for the crusade - some went by sea, some by land. As they marched East, they attracted further supporters along the way.
By the time they got to Constantinople however, the wonder on the European faces must have been apparent - they appeared to have as little in common with the Byzantine Empire than with the Muslims, not only racially, but even in language. The Byzantine Christians did not recognize the Pope, spoke Greek instead of Latin and had distinctly Middle Eastern art and architectural forms.
Those Crusaders who marched overland from France also took the opportunity to wage an anti-Semitic pogrom at groups of Jews who had settled along the Rhine River, associating the Semites in France and Germania with the Semites they were marching against in Jerusalem.
Finally the various groups made their entrance to Constantinople - and then proceeded to march by foot across Turkey to Jerusalem. An army estimated to be between 25,000 and 30,000 strong went to war in what is today Syria, Lebanon and Israel.
THE SIEGE OF ANTIOCH - THE FIRST GREAT WHITE VICTORY
The city of Antioch, (now known as Antakya in Turkey) had been founded in 300 BC by Seleucus I, Alexander the Great's famous general who had established the Seleucid Kingdom of Syria. Under the Roman Empire, Antioch became the third most important city in the world, after Rome and Constantinople itself. The city however fell to the Nonwhite Islamics in 1085 AD.
Antioch lay on the path to Palestine - the Crusaders could not hope to take possession of the latter land without first taking the fortress of Antioch - and as such it became one of the earliest major targets for the White army.
As the Crusaders approached Antioch, the Muslim defenders under Turcoman Yagji-Shah started killing all the remaining Whites in the city, along with any Nonwhite Christians who had the misfortune to be present. This set the scene for the Battle of Antioch, and the White Crusaders repaid the Nonwhite Muslims in kind when they had the opportunity.
Antioch was a purpose built city fortress. The defenses had been built by the Roman Emperor Justinian and maintained by the Byzantines. The walls were immense, with four hundred towers so spaced that every part of the wall was within bow shot. The final fortification was the citadel which rose 1000 feet above the city, a masterpiece of late Roman engineering.
Suffering deprivations of food and the inhospitable terrain, the White army settled down to a 15 month siege of the city. Fighting off two Muslim relief attempts, the Crusaders then managed to obtain supplies to build two forts, which they used to completely cut off all supply routes to the city.
Even so they could not break the city walls. Entrance was gained thanks to the treachery of an Armenian converted to Islam who was in charge of one of the towers. The Armenian let an advance party of Crusaders into the city who then opened the main gates for the rest of the White army.
By nightfall of 3 June 1099, the city was in White hands - and every Nonwhite who had foolishly remained behind in the city was dead. The first great victory of the Crusade had been won and the Crusaders then drew up their forces for their assault on their real target - Jerusalem itself.
THE CAPTURE OF JERUSALEM
The city walls of Jerusalem had originally been built by the Roman Emperor Hadrian, and, like Antioch, had been improved upon and repaired by both the Byzantines and the newer Muslim occupiers of the city. The city's water supply was from the original Roman drainage system which was still working in the 20th Century.
The governor of Jerusalem, Iftikhar ad-Duala, was confident he could hold off the Crusaders until a relief army arrived from Islamic held Egypt. He had Arab and Sudanese troops defending the immense walls, and he had taken the precaution of poisoning all but one of the water wells outside the city walls before the White army arrived. That one well was in an exposed position in clear shot of the city walls. Many Whites were killed trying to draw water, as the Muslims had planned.
In addition to that, he had ejected all the Christian - White or Nonwhite - residents of the city, only allowing the Jews of Jerusalem to stay - a move which would have dire consequences for them.
The Crusaders started their siege of Jerusalem on 7 June 1099. Suffering terrible deprivations of food and water, they nonetheless kept up their assaults on the city, gradually wearing down the defenders despite the latter's stronger position. After several attempts to breach the walls with brute force and ladders, the Crusaders were supplied with building material and wood which they managed to scavenge for the surrounding sparsely vegetated countryside.
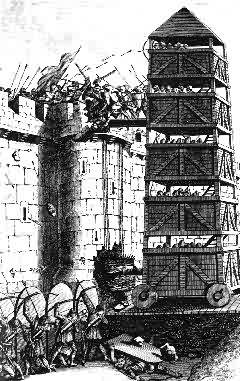
White knights laying siege to the city of Jerusalem during the First Crusade. After scavenging wood from the surrounding countryside, they built three siege towers, out of sight of the city's defenders, and used them in a night attack on the huge walls. The Muslims were astounded to see the siege towers, built as they were out of the very basic materials available on the spot.
Finally three siege towers were built - out of sight of the besieged city's Nonwhite garrison - and wheeled into place on the night of 13 July, to the recorded great astonishment of the city's defenders. Some 13,000 White soldiers then stormed the walls, suffering heavy losses. At last on midday of the 14th July, after over 16 hours of non stop fighting, a part of the wall was taken. With a breach secured, ordinary ladders were then used to pour men over the wall, and into the city itself.
Seeing the defenses collapse, the defenders retreated into the citadel, but the small surviving Muslim garrison negotiated the terms of their surrender - which included safe passage out of the city. They were the only Muslims to survive the fall of Jerusalem - the Crusaders, overjoyed and enraged at the same time for having at last won the city after so much suffering, proceeded to slaughter every Muslim they could find, men, women and children alike. According to the account of one Crusader, Raymond of Aguilers, the next morning when he went to visit the Temple area he had to work his way through corpses and blood that reached his knees.
The Jews had in the interim fled to their main synagogue. Accusing them of aiding the Nonwhite Muslims - an accusation that had fact to it - the Crusaders showed the Jews no mercy. The synagogue was burnt down with every single Jew in Jerusalem dying in the inferno.
GODFREY OF BOUILLON - THE NORDIC KING OF JERUSALEM
The Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem was then established under two Frankish nobles, Godfrey of Bouillon, and his brother Baldwin. In addition, three other states were founded: the County of Tripoli, in modern Lebanon; the Principality of Antioch, in modern Syria; and the County of Edessa, in modern northern Syria and southern Turkey.
However, the Crusader states did not try to change the population make-up of the region by enforced migration or expulsion - nor did they even try to convert the natives. So it was that the first European colonies were created: ironically in the areas where once their now very distant racial cousins had once walked.
THE SECOND CRUSADE (1147 - 1148 AD) - MILITARY FAILURE
The First Crusade's success stunned the Muslims, built as it was on a combination of zeal and luck. Maintaining the Crusader states was more difficult - the foremost problem facing the White colonists was that they were completely dependent on White European recruits to man the forts and emplacements, surrounded as they were in a sea of dark Muslim faces.
Finally in 1144, Islamic armies stormed a major city, Edessa, on the Euphrates River. The Muslim world had announced its counter attack, and the Second Crusade was called by Pope Eugenius III. This time a large number of Christian sovereigns themselves joined the crusade - the German Holy Roman Emperor Conrad III and France's King Louis VII.
Conrad made the mistake of choosing the land route from Constantinople to Palestine, and a Muslim attack in Turkey destroyed his army. Louis' army was also the victim of numerous Muslim attacks, and although depleted, was the only major force to actually reach Jerusalem in 1148. An attempt to attack the city of Damascus was made - it failed and the French army gave up and returned home.
Following the failure of the Second Crusade, the Muslim armies launched a renewed assault on Jerusalem, capturing the city in 1187. So ended the Second Crusade - with heavy White casualties and military failure in the Middle East itself.
However, in what was later to become a pattern, the White English army, which had originally meant to take part in the crusade, stopped in what is now Portugal and instead attacked the Muslim occupied city of Lisbon, helping to drive out the Moors from northern Portugal. This was significant as it showed that the Crusades were now a war against Nonwhite Islamics anywhere they could be found - not specifically against Muslims in Jerusalem.
Various holy orders of knights who took part in the Crusades were formed. The most famous being the Knights of St. John of Jerusalem, called Hospitalers, and the Poor Knights of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, called Templars.
THE THIRD CRUSADE (1189 - 1192 AD)
The failure of the Second Crusade caused a new crusade to be planned. Three White Christian kings announced their personal intentions of joining the fray: Richard I, the Lion-Hearted of England; Philip II of France; and Frederick I, called Frederick Barbarossa, the Holy Roman Emperor. Frederick Barbarossa, old and famous, died in 1189 on the way to Palestine and most of his army returned to Germany following his death. Philip II and his army returned in 1191, not having achieved any significant military successes - only Richard remained to do battle with the Nonwhites.
The Third Crusade failed however to take Jerusalem, instead seizing a number of cities along the Mediterranean coast. When Richard left the Middle East in 1192, a large part of Palestine - with the exception of Jerusalem - was back in Christian hands.

An illustration from a medieval manuscript showing Saladin wresting the cross from King Richard during the Third Crusade.
THE FOURTH CRUSADE (1201 - 1204)
Despite the exploits of Richard and the Third Crusade becoming legendary, the city of Jerusalem was never to be retaken by force of arms - only by diplomacy. This was despite Pope Innocent III calling for another crusade in 1199 to recapture Jerusalem.
This Fourth Crusade fell apart however before it began. The ruler of Venice agreed to transport French and Flemish Crusaders to Palestine - for a fee. Unable to pay this fee, the Crusaders struck a deal with the Venetians - they would help the Venetians to attack one of the city state's rivals, Zara, a Hungarian trading port on the Adriatic Sea, in return for passage to Palestine.
When Innocent III learned of the deal, he excommunicated the Crusaders - but the combined Venetian/French/Flemish force captured Zara in 1202. Unleashed of obligation to serve Rome, the Fourth Crusade turned into a free-for-all, with the participants finally attacking Constantinople, with which they had as little in common as with Jerusalem.
The city fell on 13 April 1204, and for three days the Crusaders sacked the city. The Latin Empire of Constantinople was established, which lasted until the recapture of Constantinople by the Byzantine emperor in 1261. This Fourth Crusade - which was completely diverted away from its original purpose - also saw the creation of several new Crusader states in Greece and along the Black Sea.
THE CHILDREN'S CRUSADE (1212) - RESULTS IN SLAVERY FOR CHILDREN
Although not formally listed by historians as one of the seven crusades, the Children's Crusade was nevertheless a pathetic attempt by approximately 30,000 White children to conquer the so called "holy land" of Palestine after the failure of the Fourth Crusade.
Believing that the Christian God would not abandon them, the youths Stephen of Vendrone (France) and Nicholas of Cologne (Germany) organized a crusade of children to save the "holy land" - this crusade never reached further than the southern Mediterranean coast when most of the children - all under the age of 18 - were captured and sold into slavery by Arabic pirates.
The Children's Crusade stands as one of the worst blots on the book of Christianity, along with the civil wars of the reformation era.
THE FIFTH CRUSADE (1228 - 1229)
The German Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II, undertook to start a new Crusade in 1215, but domestic political reasons caused him to delay the start. Finally he sailed from Italy in 1227, but sickness caused him to return to port after a few days.
The Pope promptly excommunicated him for the continual delays. Despite this snub, Frederick sailed for Palestine in 1228 once again. Instead of fighting, Frederick landed his impressive army and through a combination of negotiations and blackmail with his army standing ready, actually managed to negotiate a peace treaty with the Muslims. In terms of this treaty, Jerusalem was returned to the Christians and a ten year cessation of hostilities was agreed.
THE SIXTH CRUSADE (1248 - 1254) - LOST BY FLOOD
In 1248 King Louis IX of France undertook a personal six year long crusade. The center of Muslim power had by now shifted to Egypt and Louis went straight there: any Muslim settlement anywhere was now fair game. Louis landed in Egypt in 1249 and quickly captured a significant beachhead in that country.
In 1250, he launched an attack on Cairo itself - and was badly defeated - not by force of arms, but by the Nile River irrigation system first invented by the very first great White Egyptian King, Menes, thousands of years previously. Waiting until the French army was in a vulnerable position, the Muslims opened the sluice gates, creating an artificial flood which trapped Louis, forcing him to surrender.
After paying a huge ransom and surrendering his beachhead on the Egyptian coast, the Muslims let Louis go free. He then went to Palestine and for the next four years spent his time building fortifications before returning to France in 1254.
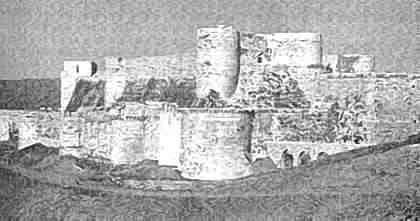
A Crusader built castle - Krak des Chevalier in Syria, mid 12th century. The Crusaders' failure to majority populate the areas they conquered with their own racial kind led to their disappearance in a very short while - so that now only their vast empty buildings stand as monuments to the spirit and heroism of the times.
THE SEVENTH CRUSADE (1270)
Louis was however clearly unhappy with his disastrous expedition to Egypt, and in 1270 he organized the last crusade. Raising a smaller army than before, Louis proceeded to launch an attack on the Muslim stronghold in Tunisia on the north African coast, at the site of the ancient city of Carthage. The Crusade was proceeding as planned when all of a sudden Louis died of natural causes in Tunisia - his army then lost the will to fight and returned to France.
The Crusader states established in the Muslim world did not last long. Hopelessly outnumbered in a sea of Nonwhite foes, they were quickly reduced in size to a few major fortifications, and then finally the last major fort city, Acre, was overrun by Islamic armies in 1291.
THE AFTER EFFECTS OF THE CRUSADES
On a strict military level the Crusades were a failure and did not dislodge the Muslims from anywhere except in northern Portugal. However, this is an unfair dismissal of the efforts of the White nations who took part in the wars. The obstacles they had to overcome were formidable - vast distances, their total reliance on soldiers recruited voluntarily from mainland Europe, combined with the extremely poor communications and supply routes of the time; makes the fact that they were able to launch expeditions of this nature so far from home, a remarkable achievement all by itself.
The Crusades also had the effect of adding to the fervor to expel the Muslim Nonwhite occupiers of Spain from the European continent - something which was finally achieved in just under 150 years after the last Crusade.
or back to
or
All material (c) copyright Ostara Publications, 1999.
Re-use for commercial purposes strictly forbidden.