 (alpha) for space loss. Most
textbooks don't develop the radar equation to its most usable
form as does this reference handbook, therefore the concept of "a"
just isn't covered.
(alpha) for space loss. Most
textbooks don't develop the radar equation to its most usable
form as does this reference handbook, therefore the concept of "a"
just isn't covered.
The radar and Electronic Warfare communities generally accept some commonly used notation for the various parameters used in radar and EW calculations. For instance, "P" is almost always power and "G" is almost always gain. Textbooks and reference handbooks will usually use this common notation in formulae and equations.
A significant exception is the use of "a" or  (alpha) for space loss. Most
textbooks don't develop the radar equation to its most usable
form as does this reference handbook, therefore the concept of "a"
just isn't covered.
(alpha) for space loss. Most
textbooks don't develop the radar equation to its most usable
form as does this reference handbook, therefore the concept of "a"
just isn't covered.
Subscripts are a different matter. Subscripts are often whatever seems to make sense in the context of the particular formula or equation. For instance, power may be "P", "PT", "Pt", or maybe "P1". In the following list, generally accepted notation is given in the left hand column with no subscripts. Subscripted notation in the indented columns is the notation used in this handbook and the notation often (but not always) used in the EW community.
 = Space loss
= Space loss 1 = One way space loss, transmitter
to receiver
1 = One way space loss, transmitter
to receiver 2 = Two way space loss, transmitter
to target (including radar cross section) and back to the receiver
2 = Two way space loss, transmitter
to target (including radar cross section) and back to the receiver 1t = One way space loss, radar
transmitter to target, bistatic
1t = One way space loss, radar
transmitter to target, bistatic 1r = One way space loss, target to
radar receiver, bistatic
1r = One way space loss, target to
radar receiver, bistatic tm may be used to clarify
specific losses, in this case the space loss between a
target and missile seeker, which could also be identified as
tm may be used to clarify
specific losses, in this case the space loss between a
target and missile seeker, which could also be identified as
 1r.
1r.
BF = Bandwidth reduction factor (jamming spectrum wider than the receiver bandwidth)
BW = Beamwidth (to 3 dB points)
c = Speed of Light
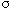 = Gain of reflected radar signal due to radar cross section
= Gain of reflected radar signal due to radar cross section
k = Boltzmann Constant
K1,2,3,4 = Proportionality constants
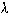 = Lambda, Wavelength or piosson factor
= Lambda, Wavelength or piosson factor
L = Loss (due to transmission lines or circuit elements)
N = Receiver equivalent noise input (kToB)
NF = Noise figure
Pi = 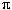 ( 3.141592654+)
( 3.141592654+)
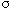 = Sigma, radar cross section (RCS)
= Sigma, radar cross section (RCS)