Measuring the electromagnetic spectrum
You actually know more about it than you may think! The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is just a name that scientists give a bunch of types of radiation when they want to talk about them as a group. Radiation is energy that travels and spreads out as it goes-- visible light that comes from a lamp in your house or radio waves that come from a radio station are two types of electromagnetic radiation. Other examples of EM radiation are microwaves, infrared and ultraviolet light, X-rays and gamma-rays. Hotter, more energetic objects and events create higher energy radiation than cool objects. Only extremely hot objects or particles moving at very high velocities can create high-energy radiation like X-rays and gamma-rays. Here are the different types of radiation in the EM spectrum, in order from lowest energy to highest:
|
Radio: yes, this is the same kind of energy that radio stations emit into the air for your boom box to capture and turn into your favorite Mozart, Madonna, or Coolio tunes. But radio waves are also emitted by other things ... such as stars and gases in space. You may not be able to dance to what these objects emit, but you can use it to learn what they are made of. |
| Microwaves: they will cook your popcorn in just a few minutes! In space, microwaves are used by astronomers to learn about the structure of nearby galaxies, including our own Milky Way! | |
| Infrared: we often think
of this as being the same thing as 'heat',
because it makes our skin feel warm. In space, IR light maps the
dust between stars. Visible: yes, this is the part that our eyes see. Visible radiation is emitted by everything from fireflies to light bulbs to stars ... also by fast-moving particles hitting other particles. Ultraviolet: we know that the Sun is a source of ultraviolet (or UV) radiation, because it is the UV rays that cause our skin to burn! Stars and other "hot" objects in space emit UV radiation. | |
| X-rays: your doctor uses them to look at your bones and your dentist to look at your teeth. Hot gases in the Universe also emit X-rays . | |
| gamma-rays: radioactive materials (some natural and others made by man in things like nuclear power plants) can emit gamma-rays. Big particle accelerators that scientists use to help them understand what matter is made of can sometimes generate gamma-rays. But the biggest gamma-ray generator of all is the Universe! It makes gamma radiation in all kinds of ways. |
A Radio Wave is not a Gamma-Ray, a Microwave is not an X-ray ... or is it?
| Radio waves, visible light, X-rays, and all the other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are fundamentally the same thing, electromagnetic radiation. |
We may think that radio waves are completely different physical objects or events than gamma-rays. They are produced in very different ways, and we detect them in different ways. But are they really different things? The answer is 'no'. Radio waves, visible light, X-rays, and all the other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are fundamentally the same thing. They are all electromagnetic radiation.
Electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of a stream of photons, which are massless particles each traveling in a wave-like pattern and moving at the speed of light. Each photon contains a certain amount (or bundle) of energy, and all electromagnetic radiation consists of these photons. The only difference between the various types of electromagnetic radiation is the amount of energy found in the photons. Radio waves have photons with low energies, microwaves have a little more energy than radio waves, infrared has still more, then visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, and ... the most energetic of all ... gamma-rays.
|
|
| The electromagnetic spectrum can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength, or frequency. |
Actually, the electromagnetic spectrum can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength, or frequency. Each way of thinking about the EM spectrum is related to the others in a precise mathematical way. So why do we have three ways of describing things, each with a different set of physical units? After all, frequency is measured in cycles per second (which is called a Hertz), wavelength is measured in meters, and energy is measured in electron volts.
The answer is that scientists don't like to use big numbers when they don't have to. It is much easier to say or write "two kilometers or 2 km" than "two thousand meters or 2,000 m". So generally, scientists use whatever units are easiest for whatever they are working with. In radio astronomy, astronomers tend to use wavelengths or frequencies. This is because most of the radio part of the EM spectrum falls in the range from a about 1 cm to 1 km, and 1 kilohertz (kHz) to 1 megahertz (MHz). The radio is a very broad part of the EM spectrum. Infrared astronomers also use wavelength to describe their part of the EM spectrum. They tend to use microns (or millionths of meters) for wavelengths, so that they can say their part of the EM spectrum falls in the range 1 to 100 microns. Optical astronomers use wavelengths as well. In the older "CGS" version of the metric system, the units used were angstroms. An Angstrom is equal to 0.0000000001 meters (10-10 m in scientific notation)! In the newer "SI" version of the metric system, we think of visible light in units of nanometers or 0.000000001 meters (10-9 m). In this system, the violet, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red light we know so well has wavelengths between 400 and 700 nanometers. This range is only a small part of the entire EM spectrum, so you can tell that the light we see is just a little fraction of all the EM radiation around us! By the time you get to the ultraviolet, X-ray, and gamma-ray regions of the EM spectrum, lengths have become too tiny to think about any more. So scientists usually refer to these photons by their energies, which are measured in electron volts. Ultraviolet radiation falls in the range from a few electron volts (eV) to a about 100 eV. X-ray photons have energies in the range 100 eV to 100,000 eV (or 100 keV). Gamma-rays then are all the photons with energies greater than 100 keV.
Show me a chart of the wavelength, frequency, and energy regimes of the spectrum !
Why Do We Have to Go to Space to See All of the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
Electromagnetic radiation from space is unable to reach the surface of the Earth except at a very few wavelengths, such as the visible spectrum and radio frequencies. Astronomers can get above enough of the Earth's atmosphere to observe at some infrared wavelengths from mountain tops or by flying their telescopes in an aircraft. Experiments can also be taken up to altitudes as high as 35 km by balloons which can operate for months. Rocket flights can take instruments all the way above the Earth's atmosphere for just a few minutes before they fall back to Earth, but a great many important first results in astronomy and astrophysics came from just those few minutes of observations. For long-term observations, however, it is best to have your detector on an orbiting satellite ... and get above it all!
The vertical illustration of the different regions of the e-m spectrum and their common uses was done by Design at Work for the curriculum supplement "Human Physiology in Space" by Barbara F. Lujan and Ronald J. White, 1994.
Glossary:
- Angstrom: A unit of length equal to 0.00000001 centimeters. This may also be written as 1 x 10-8 cm. (see scientific notation)
- Astronomy: The scientific study of matter in outer space, especially the positions, dimensions, distribution, motion, composition, energy, and evolution of celestial bodies and phenomena.
- Astrophysics: The part of astronomy that deals principally with the physics of stars, stellar systems, and interstellar material.
- Atmosphere: The gas that surrounds a planet or star. The Earth’s atmosphere is made up of mostly nitrogen, while the Sun’s atmosphere consists of mostly hydrogen.
- Dust: Not the dust one finds around the house (which is typically fine bits of fabric, dirt, and dead skin cells). Rather, irregularly shaped grains of carbon and/or silicates measuring a fraction of a micron across which are found between the stars. Dust is most evident by its absorption, causing large dark patches in regions of our Milky Way Galaxy and dark bands across other galaxies.
- Electron Volt: The change of potential energy experienced by an electron moving from a place where the potential has a value of V to a place where it has a value of (V+1 volt). This is a convenient energy unit when dealing with the motions of electrons and ions in electric fields; the unit is also the one used to describe the energy of X-rays and gamma rays. A keV (or kiloelectron volt) is equal to 1000 electron volts. An MeV is equal to one million electron volts. A GeV is equal to one billion (109) electron volts. A TeV is equal to a million million (1012) electron volts.
- EM Spectrum: The full range of frequencies, from radio waves to gamma rays, that characterizes light.
- EM Waves: Another term for light. Light waves are fluctuations of electric and magnetic fields in space.
- Frequency: A property of a wave that describes how many wave patterns or cycles pass by in a period of time. Frequency is often measured in Hertz (Hz), where a wave with a frequency of 1 Hz will pass by at 1 cycle per second.
- Gamma Ray: The highest energy, shortest wavelength electromagnetic radiations. Usually, they are thought of as any photons having energies greater than about 100 keV. (It's "gamma-ray" when used as an adjective and "gamma ray" when used as a noun.)
- Hertz: The derived SI unit of frequency, defined as a frequency of 1 cycle per second.
- Infrared: Electromagnetic radiation at wavelengths longer than the red end of visible light and shorter than microwaves (roughly between 1 and 100 microns). Almost none of the infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum can reach the surface of the Earth, although some portions can be observed by high-altitude aircraft (such as the Kuiper Observatory) or telescopes on high mountaintops (such as the peak of Mauna Kea in Hawaii).
- Matter: A word used for any kind of stuff which contains mass.
- Meter: The fundamental SI unit of length, defined as the length of the path traveled by light in vacuum during a period of 1/299 792 458 s. A unit of length equal to about 39 inches. A kilometer is equal to 1000 meters.
- Microwave: Electromagnetic radiation which has a longer wavelength (between 1 mm and 30 cm) than visible light. Microwaves can be used to study the Universe, communicate with satellites in Earth orbit, and cook popcorn.
- Radiation: Energy emitted in the form of waves (light) or particles (photons).
- Orbit: The path of an object that is moving around a second object or point.
- Photon: The smallest (quantum) unit of light/electromagnetic energy. Photons are generally regarded as particles with zero mass and no electric charge.
- Radio Waves: Electromagnetic radiation which has the lowest frequency, the longest wavelength, and is produced by charged particles moving back and forth; the atmosphere of the Earth is transparent to radio waves with wavelengths from a few millimeters to about twenty meters.
- Satellite: A body that revolves around a larger body. For example, the moon is a satellite of the earth.
- Scientific Notation: A compact format for writing very large or very small numbers, most often used in scientific fields. The notation separates a number into two parts: a decimal fraction, usually between 1 and 10, and a power of ten. Thus 1.23 x 104 means 1.23 times 10 to the fourth power or 12,300; 5.67 x 10-8 means 5.67 divided by 10 to the eighth power or 0.0000000567.
- Second: The fundamental SI unit of time, defined as the period of time equal to the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom. A nanosecond is equal to one-billionth (10-9) of a second.
- SI: The coherent and rationalized system of units, derived from the MKS system (which itself is derived from the metric system), in common use in physics today. The fundamental SI unit of length is the meter, of time is the second, and of mass is the kilogram.
- Spectrum: A plot of the intensity of light at different frequencies. Or the distribution of wavelengths and frequencies.
- Speed of Light: The speed at which electromagnetic radiation propagates in a vacuum; it is defined as 299 792 458 m/s (186,000 miles/second). Einstein’s Theory of Relativity implies that nothing can go faster than the speed of light.
- Star: A large ball of gas that creates and emits its own radiation.
- Ultraviolet: Electromagnetic radiation at wavelengths shorter than the violet end of visible light; the atmosphere of the Earth effectively blocks the transmission of most ultraviolet light.
- Universe: Everything that exists, including the Earth, planets, stars, galaxies, and all that they contain; the entire cosmos.
- Visible: Electromagnetic radiation at wavelengths which the human eye can see. We perceive this radiation as colors ranging from red (longer wavelengths; ~ 700 nanometers) to violet (shorter wavelengths; ~400 nanometers.
- Wavelength: The distance between adjacent peaks in a series of periodic waves. Also see electromagnetic spectrum.
- X ray: Electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength and very high-energy; X-rays have shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet light but longer wavelengths than gamma rays.
More about the Electromagnetic Spectrum
As it was explained in the Electromagnetic Spectrum - Level 1, electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of a stream of photons, each traveling in a wave-like pattern, moving at the speed of light and carrying some amount of energy. It was pointed out that the only difference between radio waves, visible light, and gamma-rays is the energy of the photons. Radio waves have photons with low energies, microwaves have a little more energy than radio waves, infrared has still more, then visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma-rays.
Actually, the amount of energy a photon has makes it sometimes behave more like a wave and sometimes more like a particle. This is called the " wave-particle duality" of light. It is important to understand that we are not talking about a difference in what radiation IS, but only in how it behaves. Low energy photons (such as radio) behave more like waves, while higher energy photons (such as X-rays) behave more like particles. This is an important difference for scientists to know when they design detectors and telescopes to try to 'see' EM from very low to very high energies. In fact, scientists choose whichever description of light they need for their study.
The truth is, the electromagnetic spectrum can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength, or frequency. Each way of thinking about the EM spectrum is related to the others in a precise mathematical way. The relationships are:
the wavelength equals the speed of light divided by the frequency and
or
lambda = c / nu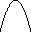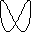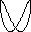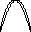
energy equals Planck's constant times the frequency (lambda and nu are just letters from the Greek alphabet that scientists like to use rather than l or f. It just helps them to keep things straight!) Both the speed of light and Planck's constant are, well, constant: They never change their values. Ever. The speed of light is equal to 299,792,458 m/s (186,000 miles/second). Planck's constant is equal to 6.626 x 10-27 erg-seconds.
or
E = h x nuSpace Observatories in Different Regions of the EM Spectrum
Radio observatories
At present, there is one radio observatory in space. There are plans, however, for one more in the next year. The Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) Space Observatory Program (VSOP) is a Japanese mission that launched in February 1997. RADIOASTRON, a Russian mission, is scheduled for 1998. NASA will be supporting both missions with its Deep Space Network radio telescope facilities around the world.Radio waves CAN make it through the Earth's atmosphere without significant obstacles (In fact radio telescopes can observe even on cloudy days!). However, the availability of a space radio observatory complements radio telescopes on the Earth in some important ways.
One is a special technique used in radio astronomy called "interferometry". Radio astronomers can combine data from two telescopes that are very far apart and create images which have the same resolution as if they had a single telescope as big as the distance between the two telescopes! That means radio telescope arrays can see incredibly small details. One such array is called the Very Large Baseline Array (VLBA): it consists of ten radio telescopes which reach all the way from Hawaii to Puerto Rico: nearly a third of the way around the world! By putting a radio telescope in orbit around the Earth, radio astronomers could make images as if they had a radio telescope the size of the entire planet!
Microwave observatories
Scheduled for launch in the Fall of 2000 is the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP). MAP will measure the temperature fluctuations of the cosmic microwave background radiation over the entire sky in order to address such fundamental questions as:- What are the values of the cosmological parameters of the Big Bang theory?
- How did structures of galaxies form in the Universe?
- When did the first structure of galaxies form?
The sky is a source of microwaves in every direction, most often called the microwave background. This background is believed to be the remnant from the "Big Bang" scientists believe our Universe began with. It is believed that a very long time ago all of space was scrunched together in a very small, hot ball. The ball exploded outward and became our Universe as it expanded and cooled. Over the course of the past several billion years (the Universe's actual age is still a matter of debate, but is believed to be somewhere between ten and twenty billion years), it has cooled all the way to just three degrees above zero. It is this "three degrees" that we measure as the microwave background.
COBE mapped out the entire microwave background, carefully measuring very small differences in temperatures from one direction to another. Astronomers have many theories about the beginning of the Universe and their theories predict how the microwave background would look. The very precise measurements made by COBE eliminated a great many of the theories about the Big Bang.
Infrared observatories
The biggest infrared observatory currently in orbit is the brand new Infrared Space Observatory (ISO), launched in November 1995 by the European Space Agency. ISO will operate for at least two years barring unforeseen circumstances. It has been placed in an elliptical orbit with a 24 hour period which keeps it in view of the ground stations at all times, a necessary arrangement since ISO transmits observations as it makes them rather than storing information for later playback. ISO will able to observe from 2.5 to 240 microns.Early in the next decade, NASA will be launching the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). SIRTF will use an passive cooling system (i.e. it radiates away its own heat rather than requiring an active refrigerator system like most other space infrared observatories) and it will be launched well away from the Earth where it will not have to contend with Earth occultation of sources nor with the comparatively warm environment in near-Earth space.
Another major infrared facility coming soon will be the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA). Although SOFIA will not be an orbiting facility, it will carry a large telescope within a 747 aircraft flying at an altitude sufficient to get it well above most of the Earth's infrared absorbing atmosphere. SOFIA will be replacing the Kuiper Airborne Observatory.
Visible spectrum observatories
The only visual observatory in orbit at the moment is the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Like radio observatories in space, there are visible observatories already on the ground. However, Hubble has several special advantages over them.HST's biggest advantage is, because it is above the Earth's atmosphere, it does not suffer distorted vision from the air. If the air was all the same temperature above a telescope and there was no wind (or the wind was perfectly constant), telescopes would have a perfect view through the air. Alas, this is not how our atmosphere works. There are small temperature differences, wind speed changes, pressure differences, and so on. This causes light passing through air to suffer tiny wobbles. It gets bent a little, much like light gets bent by a pair of glasses. But unlike glasses, two light beams coming from the same direction do not get bent in quite the same way. You've probably seen this before -- looking along the top of the road on a hot day, everything seems to shimmer over the black road surface. This blurs the image telescopes see, limiting their ability to resolve objects. On a good night in an observatory on a high mountain, the amount of distortion caused by the atmosphere can be very small. But the Space Telescope has NO distortion from the atmosphere and its perfect view gives it many many times better resolution than even the best ground-based telescopes on the best nights.
Another advantage of the Space Telescope is that without the atmosphere in the way, it can see more than just the visible spectrum. The Space Telescope can also see ultraviolet light which normally is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be seen by regular telescopes. So the Space Telescope can see a much wider portion of the spectrum.
Ultraviolet observatories
Right now there are no dedicated ultraviolet observatories in orbit. The Hubble Space Telescope can perform a great deal of observing at ultraviolet wavelengths, but it has a very fairly small field of view. Until September 1996, the International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was operating and observing ultraviolet radiation. Its demise, although unfortunate, was hardly premature: IUE was launched in January, 1978 with planned operations of three years. IUE functioned more or less like a regular ground based observatory save that the telescope operator and scientist did not actually visit the telescope, but sent it commands from the ground. Other than some care in the selection of materials for filters, a UV telescope like IUE is very much like a regular visible light telescope.In addition to IUE, there have been fairly important recent UV space missions. A reusable shuttle package called Astro has been flown twice in the cargo bay of the space shuttle: it consisted of a set of three UV telescopes. Unlike HST, the Astro UV telescopes had very large fields of view and so could take images of larger objects in the sky -- like galaxies. For instance, if the Hubble Space Telescope and the Astro telescopes were used to look at the Comet Hale-Bopp, Hubble would be able to take spectacular pictures of the core of the comet. The Astro telescopes would be able to take pictures of the entire comet, core and tail.
Extreme Ultraviolet observatories
There are two extreme ultraviolet observatories in space at the moment. One of them is the very first extreme ultraviolet observatory ever, the Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer (EUVE). Astronomers have been somewhat reluctant to explore from space at the extreme ultraviolet wavelengths since all theory strongly suggests that the interstellar medium (the tiny traces of gases and dust between the stars) would absorb radiation in this portion of the spectrum. However, when the Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer (EUVE) was launched, observations showed that the solar system is located within a bubble in the local interstellar medium. The region around the Sun is relativity devoid of gas and dust which allows the EUVE instruments to see much further than theory predicted.Another extreme ultraviolet observatory currently operating is the Array of Low Energy X-ray Imaging Sensors (ALEXIS). Although its name indicates that it is an X-ray observatory, the range of energy ALEXIS is exploring is at the very lowest end of the X-ray spectrum and often considered to be extreme ultraviolet. ALEXIS was launched in 1995 on a Pegasus XL launch vehicle, but a failure during the launch tore off one of the solar panels and the satellite is tumbling through space. The ALEXIS operations team has been working hard, however, to use the tumbling of the satellite to map out the entire sky.
X-ray observatories
There are several X-ray observatories currently operating in space with more to be launched in the next few years.The Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) was launched on December 30, 1995. RXTE is able to make very precise timing measurements of X-ray objects, particularly those which show patterns in their X-ray emissions over very short time periods, such as certain neutron star systems and pulsars.
Other X-ray observatories currently operating in space include ROSAT, a joint venture between the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom; the Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics (ASCA), a joint U.S.-Japan venture; the Kvant astrophysics module attached to the Russian space station Mir, and SAX, an Italian X-ray satellite.
NASA is planning to launch another major new X-ray astronomy satellite called the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF)in late 1998.
Gamma-ray observatories
The Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (CGRO) was launched by the space shuttle in April 1991. The observatory's instruments are dedicated to observing the gamma-ray sky, including locating gamma-ray burst sources, monitoring solar flares, and other highly energetic astrophysical phenomenon. An unexpected discovery which Compton has made was the observation of gamma-ray burst events coming from the Earth itself at the top of thunderstorm systems. The cause of this phenomenon is not known, but it is currently suspected to be related to "Sprites": lightening flashes which are occasionally seen jumping upwards from cloud tops to the upper stratosphere.The Russian gamma-ray observatory Granat has exhausted its control fuel. Its last maneuver was to initiate a roll which has allowed it to perform a continuous all-sky survey.
The next major gamma-ray mission in the near future include the joint U.S.-Russia missions Spectrum X-Gamma which will make pointed observations in both X-ray and gamma-ray wavelength regimes.
Return to Constellation-X general science pages Constellation-X Education and Outreach Home
