Nerve cells, called neurons, are the fundamental elements of the central nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of about 100 billion neurons (10 to the power 11). Neurons are much like other cells of the body in their general organization and their biochemical systems. However they also possess unique features which are crucial to the functioning of the central nervous system. In essence, a given neuron may both receive and send out signals to neighboring neurons in the form of electrical pulses. A neuron is built up of three parts: the cell body, the dendrites and the axon as shown in the figure. The body of the cell contains the nucleus of the cell and carries the biochemical transformations necessary to synthesize enzymes and other molecules necessary to the life of the neuron. It is roughly spherical or pyramidal in shape - the precise shape depending on position and function in the brain. It is typically several microns in diameter (a micron is a millionth of a meter).
Previous: Brain overview - Next: Brain operation and processes |
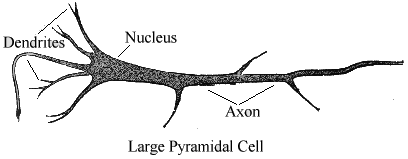 Each neuron has
a hair-like structure surrounding it - these are the dendrites. Dendrites are some
tens of microns in length. The branch out into a tree-like form around the cell body. The
dendrites are like electrical cables which serve to conduct incoming signals to the cell.
The axon or nerve fiber is the outgoing connection for signals emitted by the
neuron. It differs from the dendrites in its shape and by the properties of its external
membrane. It is usually much longer than the dendrites, varying from a millimeter (one
thousandth of a meter) to one meter. At its end it branches into smaller structures which
communicate with other neurons. The branching of the dendrites, in contrast, takes place
much closer to the cell body. Neurons are connected together at these extremities in a
complex spatial arrangement. Typically a given neuron is connected to about ten thousand
other neurons. The specific point of contact between the axon of one cell and a dendrite
of another is called a synapse.
Each neuron has
a hair-like structure surrounding it - these are the dendrites. Dendrites are some
tens of microns in length. The branch out into a tree-like form around the cell body. The
dendrites are like electrical cables which serve to conduct incoming signals to the cell.
The axon or nerve fiber is the outgoing connection for signals emitted by the
neuron. It differs from the dendrites in its shape and by the properties of its external
membrane. It is usually much longer than the dendrites, varying from a millimeter (one
thousandth of a meter) to one meter. At its end it branches into smaller structures which
communicate with other neurons. The branching of the dendrites, in contrast, takes place
much closer to the cell body. Neurons are connected together at these extremities in a
complex spatial arrangement. Typically a given neuron is connected to about ten thousand
other neurons. The specific point of contact between the axon of one cell and a dendrite
of another is called a synapse.